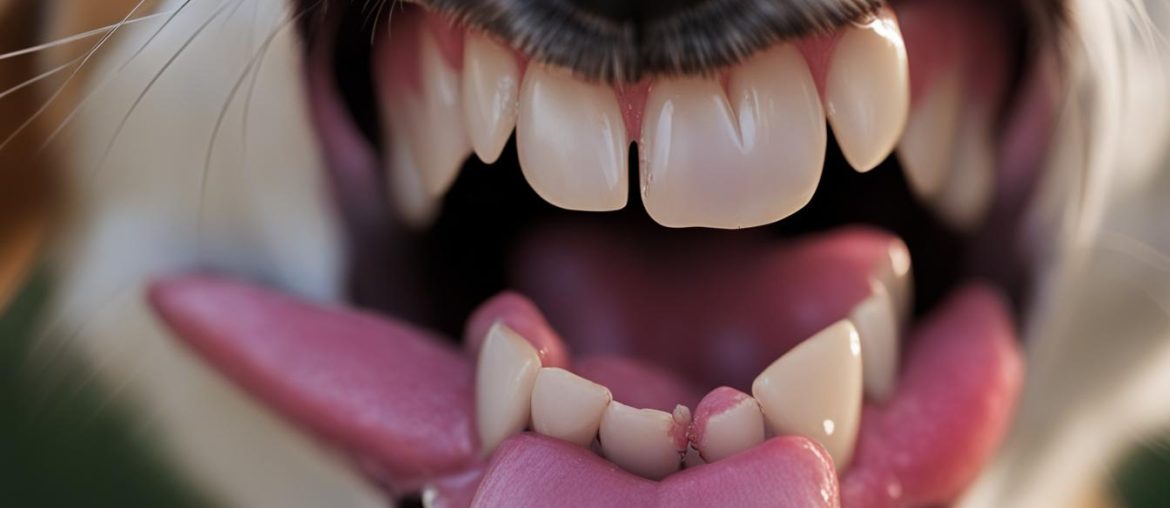
As a dog owner, it’s important to understand the dental health of your furry friend. One common question that often arises is, “Do dogs teeth grow back?” In this article, I will delve into the fascinating world of canine dental health, shedding light on the growth and loss of dogs’ teeth.
During the early stages of a puppy’s life, they develop sharp little teeth known as puppy teeth or milk teeth. These temporary teeth are gradually lost and replaced by the dog’s permanent adult teeth between 3-6 months of age. However, once the permanent teeth are in place, they do not grow back if lost or damaged.
Canine dental health is crucial for the overall well-being of your dog. Dental problems can cause pain, infection, and difficulty eating, affecting their quality of life. To ensure your dog’s oral hygiene, proper dental care is necessary, including regular brushing and veterinary check-ups.
Key Takeaways:
- Dogs’ puppy teeth are gradually replaced by permanent adult teeth between 3-6 months of age.
- Once the permanent teeth are in place, they do not grow back if lost or damaged.
- Canine dental health is important for overall well-being, as dental problems can cause pain, infection, and difficulty eating.
- Proper dental care, including regular brushing and veterinary check-ups, is necessary to maintain a dog’s oral hygiene.
Teething in Puppies: The Process of Tooth Loss and Growth

Teething is a natural process in puppies where their temporary puppy teeth are gradually replaced by permanent adult teeth. It usually begins around 3-4 weeks of age when puppies start developing their puppy teeth, also known as milk teeth. By 6-8 weeks, they have a complete set of 28 puppy teeth. However, these puppy teeth do not last long, as the permanent teeth start growing in between 3-6 months of age.
During the teething phase, puppies may experience discomfort and exhibit certain behavioral changes. They may chew excessively, drool more than usual, and even have swollen gums. It’s important to provide appropriate teething aids, such as safe chew toys and wet cloths, to alleviate their discomfort. Regular veterinary check-ups are also necessary to monitor the progress of tooth development and ensure a healthy transition from puppy teeth to permanent adult teeth.
Table: Puppy Tooth Loss and Permanent Dog Teeth
| Puppy Teeth | Permanent Adult Teeth |
|---|---|
| 28 temporary puppy teeth | 42 permanent adult teeth |
| Replace puppy teeth between 3-6 months | Complete set of adult teeth by 7 months (up to 8-9 months for large breeds) |
Proper dental care during the teething phase is crucial for maintaining a puppy’s oral health. It helps prevent dental problems, such as tooth decay and gum disease, which can lead to pain, infection, and difficulty eating. By understanding the process of tooth loss and growth in puppies, pet owners can provide the necessary care and support their furry friends need for healthy and strong permanent teeth.
Canine Teeth: The Role of Canines in Dogs’ Dentition

Canine teeth, also known as fang-like teeth, play a crucial role in a dog’s dentition. These sharp-pointed teeth are located on either side of the incisors, and they serve important functions in a dog’s daily life.
The puppy canines, also known as deciduous canines, are part of the temporary teeth set that puppies develop. They typically fall out and are replaced by permanent canines between 4-6 months old. However, the exact timing of tooth loss and replacement may vary among different breeds.
Canine teeth are vital for biting, tearing, and holding objects. They enable dogs to grip their prey, tear apart food, and defend themselves when necessary. These teeth are longer and more robust than the other types of teeth, making them perfectly suited for these tasks. A well-developed set of canines ensures that a dog can perform their natural behaviors effectively.
Puppy Canines vs. Permanent Canines
When comparing puppy canines with permanent canines, there are some distinct differences. Puppy canines are smaller, thinner, and have sharper tips compared to their adult counterparts. As puppies grow and develop, their deciduous canines are gradually replaced by more substantial and stronger permanent canines.
| Age | Puppy Canines | Permanent Canines |
|---|---|---|
| Puppyhood (3-6 months) | Smaller and thinner | Gradually growing in |
| Adulthood | Lost and replaced | Strong and well-developed |
As can be seen in the table above, the puppy canines are a temporary part of a dog’s dentition, while the permanent canines are a lifelong feature.
Dental Issues in Puppies: Early Loss and Broken Teeth

Dental issues can arise in puppies, including early loss of puppy teeth and broken puppy canines. These problems can be caused by accidents or injuries during the teething phase, resulting in discomfort and potential complications. It is important for dog owners to be aware of these dental issues and seek immediate veterinary care when necessary.
Early loss of puppy teeth can occur if a tooth is accidentally knocked out or damaged. While the permanent adult tooth will eventually grow in to replace the lost tooth, there are risks associated with early tooth loss. An empty socket from the lost tooth can become a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to infection. Additionally, the absence of a tooth can cause misalignment of incoming permanent teeth, which can further complicate dental health.
Broken puppy canines, or chipped teeth, can be extremely painful for puppies. In addition to causing discomfort, broken teeth can also increase the risk of infection. Veterinary care is essential in these cases to assess the tooth and determine the appropriate treatment. Depending on the severity of the break, a broken tooth may need to be extracted or bonded to prevent further pain and complications.
In cases of dental issues in puppies, immediate veterinary care is crucial to address the problem and prevent further complications. Early intervention can help alleviate pain, prevent infection, and ensure proper tooth development for a healthy adult dentition.
Abnormal Tooth Development: Crooked or Missing Canines

In some cases, a puppy’s permanent canines may come in crooked, misaligned, or not at all. This can be due to retained puppy teeth, trauma or injury, genetic factors, nutritional deficiencies, underlying disease, or infection. Crooked or missing canines can affect a dog’s bite and overall oral health. Veterinary dental evaluation, including X-rays, is essential to determine the underlying cause and potential treatment options, which may include extraction, orthodontic correction, or infection treatment.
| Causes of Crooked or Missing Canines | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Retained puppy teeth | Extraction of retained teeth |
| Trauma or injury | Orthodontic correction or extraction |
| Genetic factors | Orthodontic correction or extraction |
| Nutritional deficiencies | Supplementation and orthodontic correction if necessary |
| Underlying disease or infection | Treatment of the underlying condition and orthodontic correction if necessary |
Early detection and intervention are key in addressing abnormal tooth development in puppies. If you notice that your puppy’s canines are crooked, misaligned, or missing, it is important to consult a veterinarian experienced in dental care for dogs. X-rays will help determine the exact condition of the teeth and identify any underlying issues that may be causing the abnormality. Based on the diagnosis, the veterinarian will recommend the most appropriate treatment options to correct the problem.
Regular dental care and early intervention can greatly improve a dog’s oral health and prevent potential complications associated with crooked or missing canines. It is crucial to prioritize dental health and consult a veterinarian for professional guidance and treatment.
Remember, dogs rely on their teeth not only for eating, but also for chewing, playing, and interacting with the world around them. By addressing abnormal tooth development in puppies, you can help ensure your dog’s overall well-being and quality of life.
Teething Timeline and Completion in Puppies

During the teething phase, puppies go through a gradual process of tooth loss and growth as their puppy teeth are replaced by permanent adult teeth. The teething timeline in puppies typically spans from 3 to 6 months of age. At around 3 to 4 weeks old, puppies start developing their puppy teeth, also known as milk teeth. By 6 to 8 weeks, they have a complete set of 28 puppy teeth. These temporary teeth serve their purpose until the permanent adult teeth start growing in.
The completion of the teething process varies among individual puppies and breeds. Most puppies will have their full set of 42 permanent teeth by 7 months old. However, larger breeds may continue teething until 8 to 9 months old. It’s important to note that the teething process can cause discomfort for puppies, including pain, swelling, chewing, drooling, and even behavioral changes.
| Age (Months) | Teething Milestones |
|---|---|
| 3-4 | Start of teething with the eruption of puppy teeth |
| 6-8 | Complete set of 28 puppy teeth |
| 3-6 | Gradual replacement of puppy teeth with permanent adult teeth |
| 7 | Most puppies have their full set of 42 permanent teeth |
| 8-9 | Teething may continue for some larger breeds |
During the teething phase, providing appropriate teething aids, such as safe chew toys and wet cloths, can help alleviate discomfort and reduce the urge to chew on inappropriate objects. It’s also important to monitor tooth development and schedule regular veterinary dental check-ups to ensure proper oral health. Daily tooth brushing should be initiated after teething is complete to maintain good dental hygiene and prevent dental diseases in dogs.
Caring for a Teething Puppy: Remedies and Tips
Teething can be a challenging phase for puppies, but there are remedies and tips that can help alleviate their discomfort and promote healthy dental development. Here are some effective ways to care for a teething puppy:
1. Provide appropriate teething aids:
Safe and durable chew toys specifically designed for teething puppies can provide relief and satisfy their natural urge to chew. Look for toys made of high-quality materials that are free from small parts or toxic substances. Textured toys can massage sore gums, while chilled or frozen toys can help numb the area and reduce inflammation. Remember to supervise your puppy while they are chewing to prevent any accidents or choking hazards.
2. Offer wet or softened food:
During the teething phase, puppies may experience discomfort while eating hard kibble. To make mealtime easier for them, consider temporarily switching to wet or softened food. This will reduce the strain on their teeth and make it more comfortable for them to chew and swallow. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate diet for your teething puppy.
3. Massage the gums:
Gently massaging your puppy’s swollen gums with a clean finger can provide relief and help soothe the discomfort. Wash your hands thoroughly and use a circular motion to massage the gums. You can also try using a damp cloth to apply gentle pressure on the gums. This can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Remember, regular veterinary dental check-ups during the teething phase are essential to ensure proper tooth growth and development. Your veterinarian can provide additional guidance, monitor the progress of your puppy’s teeth, and address any concerns or issues that may arise. By following these remedies and tips, you can help your teething puppy navigate this phase with comfort and care.
Importance of Dental Care for Dogs’ Overall Health
Proper dental care is essential for a dog’s overall health and well-being. Just like humans, dogs can suffer from dental problems such as gum disease, tooth decay, and bad breath. Maintaining good oral hygiene in dogs is vital to prevent these issues and promote a healthy mouth.
Veterinary check-ups play a crucial role in ensuring optimal dental health for dogs. Regular dental examinations and cleanings help identify any dental issues early on and prevent further complications. These check-ups also provide an opportunity for the vet to assess the dog’s teeth and gums, recommend appropriate dental care, and address any concerns.
In addition to veterinary care, daily tooth brushing is an essential part of a dog’s dental routine. Using dog-specific toothpaste and a toothbrush or finger brush designed for pets, owners can effectively remove plaque and reduce the risk of tartar buildup. Regular brushing helps maintain healthy gums, prevents tooth decay, and keeps a dog’s breath fresh.
Incorporating dental chews, chew toys, and special diets formulated for dental health can further assist in maintaining a dog’s oral hygiene. These products help clean teeth, massage gums, and reduce plaque and tartar buildup. However, it’s important to choose safe and appropriate chew toys to avoid tooth damage or ingestion hazards.
By prioritizing dental care, dog owners can help their furry friends maintain healthy teeth and gums, preventing dental disease, tooth loss, and potential bacterial spread to other organs. A healthy mouth contributes to a dog’s overall well-being and ensures they can enjoy a pain-free, comfortable life.
Benefits of Dental Care for Dogs:
- Prevents gum disease and tooth decay
- Reduces bad breath
- Maintains healthy gums
- Prevents tooth loss
- Reduces the risk of bacterial infections
Proper Dental Care Practices for Dogs:
- Regular veterinary check-ups, including dental examinations and cleanings
- Daily tooth brushing with dog-specific toothpaste and a toothbrush or finger brush designed for pets
- Providing dental chews, chew toys, and special diets formulated for dental health
- Monitoring and addressing any signs of dental issues, such as bad breath, swollen gums, or tooth discoloration
Effects of Tooth Loss on Dogs’ Health and Well-being

Tooth loss in dogs can have significant effects on their physical health and mental well-being. When a dog loses a tooth, it can lead to various dental problems such as gum disease, tooth decay, and difficulty eating. Without proper dental care, these issues can progress and result in pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
Not only do dental problems impact a dog’s physical health, but they can also affect their overall well-being. Dogs with missing teeth may experience anxiety, irritability, decreased appetite, and changes in behavior. The pain and discomfort associated with dental issues can have a negative impact on their quality of life.
It is important for dog owners to address dental issues promptly and provide necessary dental care. Regular veterinary check-ups, including dental examinations and cleanings, are crucial for maintaining oral hygiene. Additionally, daily tooth brushing with dog-specific toothpaste and toothbrushes can help prevent dental disease and reduce the risk of tooth loss.
By prioritizing dental care, dog owners can ensure that their furry friends have healthy teeth and gums, which is essential for their overall health and well-being.
Wrapping Up
To sum up, understanding and prioritizing canine dental health is vital for dog owners. Puppies go through the teething process, during which their puppy teeth are replaced by permanent adult teeth. It is important to note that adult teeth do not grow back if lost or damaged, highlighting the significance of proper dental care.
Maintaining canine dental health requires regular dental care, including brushing their teeth, scheduling veterinary check-ups, and providing appropriate chew toys. By incorporating these practices into a dog’s routine, owners can ensure their furry companions have healthy teeth and gums throughout their lives.
Addressing dental issues promptly is crucial to prevent pain, infection, and other health problems associated with tooth loss. Neglected dental care can lead to dental diseases, such as gum disease and tooth decay, which can have detrimental effects on a dog’s overall health and well-being. Therefore, maintaining proper dental care is essential for a dog’s comfort and quality of life.
By understanding the teething process, recognizing the importance of dental care, and taking action to address dental issues, dog owners can ensure their beloved pets maintain optimal dental health. Prioritizing canine dental health is a proactive approach that contributes to the overall well-being and longevity of dogs.
FAQ
Do puppies’ teeth grow back?
No, once a puppy’s teeth are lost or damaged, they do not grow back. It is important to take care of their dental health from an early age.
How long does the teething process last in puppies?
The teething process in puppies typically lasts from 3-6 months, during which their temporary teeth are gradually replaced by permanent adult teeth.
What are canine teeth and why are they important?
Canine teeth, also known as fang-like teeth, play a crucial role in a dog’s dentition. They are important for biting, tearing, and holding objects, and their proper development is essential for a dog’s overall oral health.
What should I do if my puppy loses a tooth during teething?
If your puppy loses a tooth early due to injury or accident, it is important to seek immediate veterinary care to prevent infection and monitor the development of their permanent teeth.
What can cause crooked or missing canines in puppies?
Crooked or missing canines in puppies can be caused by retained puppy teeth, trauma or injury, genetic factors, nutritional deficiencies, underlying disease, or infection.
When does teething usually complete in puppies?
Most puppies will have their complete set of 42 permanent teeth grown in by 7 months old, with the teething process usually finishing by 8-9 months old for some large breeds.
How can I help alleviate my teething puppy’s discomfort?
Providing appropriate teething aids such as chew toys of various textures, chilled chew toys, wet cloths, and frozen treats can help relieve your teething puppy’s discomfort.
Why is dental care important for dogs?
Proper dental care is crucial for a dog’s overall health and well-being. Regular veterinary check-ups, daily tooth brushing, and providing dental chews and toys can help maintain their oral hygiene.
What are the effects of tooth loss on a dog’s health and well-being?
Tooth loss in dogs can lead to dental problems such as gum disease, tooth decay, and difficulty eating. It can also cause pain, infection, and behavioral changes in dogs.
How can I ensure my dog has healthy teeth and gums throughout their life?
By prioritizing dental care, including regular veterinary check-ups, daily tooth brushing, and providing appropriate dental aids, you can help ensure your dog maintains healthy teeth and gums.